Understanding the Lifecycle of Indoor Pests
Indoor pests have a way of transforming your cozy abode into a troublesome space, disrupting your daily life and presenting various health risks.
Understanding these pests is crucial! This article explores the intricate lifecycle of common indoor pests and the factors that influence their development. It also outlines practical prevention techniques and strategies to help you maintain a pest-free home.
Take charge today and reclaim your space!
Contents
Key Takeaways:

- Understanding indoor pest lifecycles helps you manage them effectively.
- Environmental conditions impact pest growth and survival.
- Regular pest management can minimize infestations.
Defining Common Indoor Pests
Indoor pests pose a considerable challenge for homeowners, impacting both health and property. Common culprits such as cockroaches, termites, mosquitoes, ants, and houseflies flourish in urban environments like Metro Manila, Philippines.
Grasping the nuances of these pests is essential for implementing effective pest management strategies. By doing so, you can maintain a pest-free home and protect yourself from the diseases they may carry.
Lifecycle of Indoor Pests
The lifecycle of indoor pests plays a pivotal role in their management and control. Common nuisances like cockroaches, termites, and mosquitoes progress through distinct life stages egg, larval, pupal, and adult each marked by unique biological behaviors and reproductive rates.
Grasping these stages is crucial for crafting effective pest management strategies and preventing infestations through targeted interventions. With this knowledge in hand, you can take proactive steps to maintain a pest-free environment.
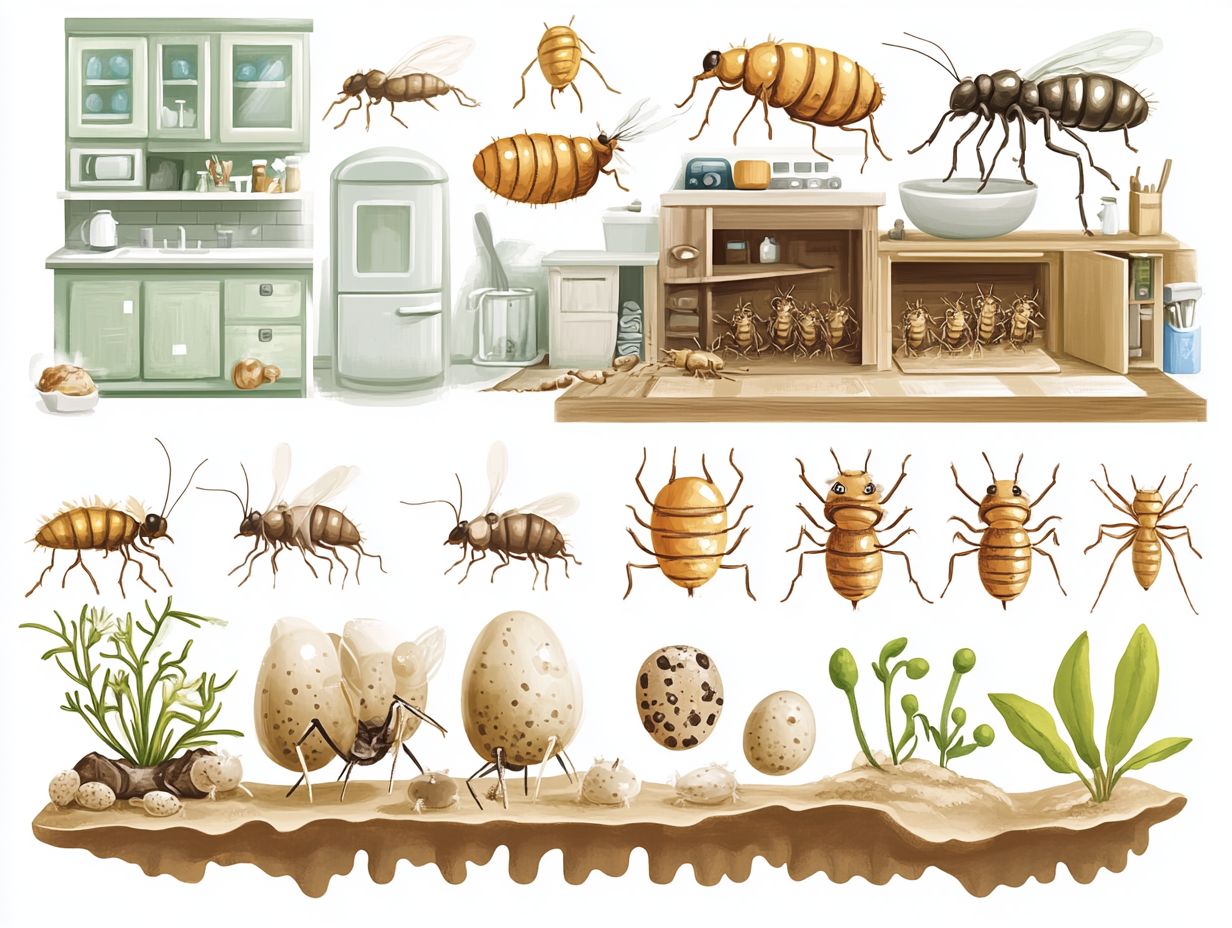
Egg Stage
The egg stage is an important first step in the lifecycle of numerous indoor pests, including cockroaches, termites, and mosquitoes. During this phase, female pests strategically lay their eggs in warm, concealed areas, effectively creating breeding grounds that are often challenging to uncover.
For example, cockroaches typically deposit their eggs in the dark, damp corners of kitchens and bathrooms. Termites may opt for damp wood or soil, allowing them to flourish in hidden locales. Mosquitoes, on the other hand, prefer to lay their eggs in stagnant water, which can be found in anything from bird baths to clogged gutters.
Several factors, including temperature, humidity, and proximity to food sources, play a significant role in the successful hatching of these eggs. By adopting simple pest control methods such as maintaining regular cleaning routines to eliminate potential hiding spots and treating standing water to disrupt mosquito reproduction homeowners can effectively mitigate the risk of pest infestations at this crucial stage.
Larval Stage
The larval stage is a crucial period for pests like cockroaches and mosquitoes, during which they experience significant growth and development. If sanitation practices aren t followed, you may witness a rapid surge in their populations, especially with mosquito larvae.
During this phase, many species display unique feeding habits that directly affect their environment. Larvae often feast on organic matter and decaying substances, creating conditions ripe for further infestations if not managed properly. The growth patterns of these larvae vary significantly among different pests; some progress through multiple molts, each one marked by a considerable increase in size and activity.
Implementing effective sanitation practices such as eliminating standing water and disposing of waste correctly is essential for controlling these populations. By doing so, you limit their ability to thrive and transition into adulthood, keeping your space pest-free.
Pupal Stage
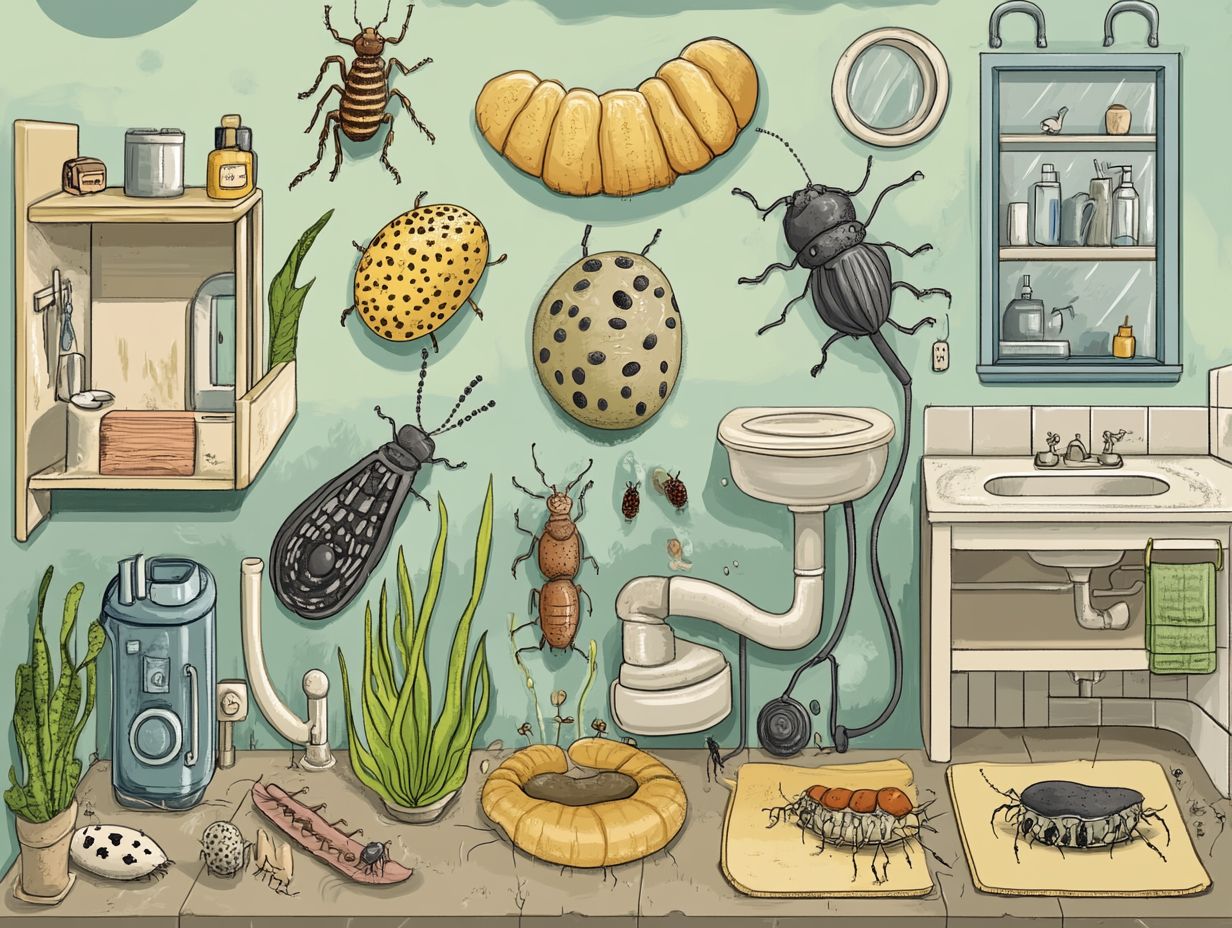

In the pupal stage, pests embark on a remarkable transformation, evolving into their adult forms. This stage is a game-changer for certain pests like mosquitoes!
During this time, pests are particularly vulnerable and less mobile. This makes them ideal targets for your control measures.
With integrated pest management (IPM) techniques using a combination of methods to control pests, such as introducing natural predators or utilizing biological control agents you can achieve impressive results.
By concentrating your efforts on the pupal stage, you can significantly diminish adult populations. This will help reduce the likelihood of future infestations.
Preventive measures, including habitat modification and targeted treatments, can help you interrupt the development cycle before adults emerge. This leads to a more sustainable approach to managing pest populations across various environments.
Adult Stage
The adult stage of pests like cockroaches and termites marks their entrance into reproductive maturity, which can significantly influence pest populations. When these adult pests are left unchecked, they can reproduce at an astonishing rate, leading to potential infestations.
These adult forms showcase distinct behaviors that facilitate their rapid population growth. For instance, they often nest in concealed areas and diligently forage for food.
A single female cockroach has the capability to produce hundreds of eggs throughout her lifetime, allowing just a few pests to escalate into a daunting infestation in no time.
Understanding their reproductive cycles is essential for effective pest management. Targeted treatments during mating seasons can help curb their proliferation.
Control methods such as baits and traps are specifically crafted to disrupt their reproductive patterns, effectively reducing future populations. Act now to stop these pests before they multiply!
Implementing preventive strategies is also vital. This includes maintaining high sanitation standards and sealing off entry points to manage these resilient pests.
Factors Affecting Pest Lifecycle
Several factors shape the lifecycle and expansion of indoor pests. Environmental conditions like temperature and humidity along with the availability of food and water sources, significantly influence pest populations and their ecological effects in urban environments.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure directly impact pest populations and their life cycles. These factors play a significant role in the ecological consequences of pest infestations. Therefore, maintaining stringent sanitation practices is essential for controlling their spread.
For example, when temperatures rise, reproduction rates of insects like aphids and mosquitoes can skyrocket, leading to rapid population growth in just a few days. On the flip side, extreme cold can drastically reduce their numbers, causing a decline in species such as the European corn borer, which prefers warmer climates.
Additionally, elevated humidity levels foster fungal growth, creating an inviting environment for pests like termites and cockroaches that thrive in damp conditions.
Understanding these environmental influences is vital for crafting effective pest management strategies. This underscores the need for proactive measures that can adapt to shifting climatic conditions.
Food and Water Sources
Food and water sources are vital for pest populations. If ignored, they can lead to infestations.
Pests like rodents, cockroaches, and flies thrive in unkempt environments. They find nourishment and hydration, leading to rapid reproduction.
Regular waste disposal, sealing entry points, and routine inspections are crucial. Understanding the link between food, water, and pest lifecycles is essential for proactive sanitation.
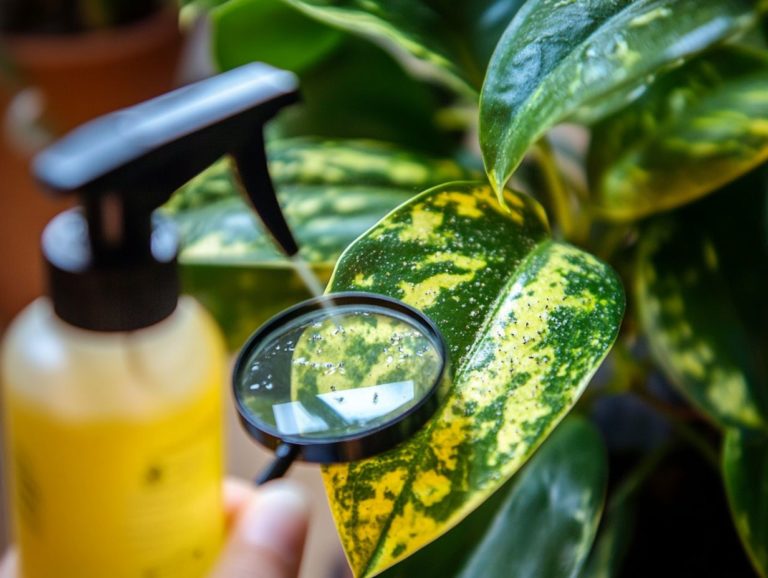
Preventing and Controlling Indoor Pests
Preventing and controlling indoor pests demands a variety of methods that seamlessly blend effective pest management strategies with essential prevention techniques. By adopting this holistic method, you can maintain pest populations at manageable levels, significantly diminishing the chances of infestations.
Effective Pest Management Strategies
Effective pest management strategies involve a range of practices designed to minimize pest populations and their impact on your home or business. A combined pest control approach emphasizes understanding the biological behaviors of specific pests, allowing you to tailor your control measures accordingly.
This approach includes different methods, such as cultural practices, mechanical barriers, and, when necessary, the careful use of chemical treatments. By recognizing the life cycles and habitats of pests, you can develop more effective prevention techniques.
Professional pest control services are essential in this framework, offering expert assessments to identify infestations early. This ensures that the strategies you implement are both efficient and environmentally friendly.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a balanced ecosystem where pests are kept in check without relying on harmful chemicals, fostering a safer and more sustainable environment for everyone involved.
Common Prevention Techniques
Use these prevention techniques to keep your home pest-free and healthy! Effective sanitation practices play a key role in reducing the availability of food and water sources for pests.
Alongside sanitation, sealing cracks and crevices around windows, doors, and foundations is crucial. Sealing these gaps keeps unwanted pests out!
Regularly inspecting and cleaning often-overlooked areas, such as basements and attics, can further deter pest infestations. You should also be mindful of your landscaping choices.
Ensure that vegetation is trimmed back and that mulch is kept at a safe distance from your home. Educating yourself on the types of pests common in your area can empower you to take proactive measures in your pest management plans, ultimately fostering a healthier living environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are indoor pests?
Indoor pests include insects and rodents that can damage your home.
What is the lifecycle of indoor pests?

The lifecycle of indoor pests refers to the stages of growth and development that these pests go through, from egg to adult, in order to reproduce and survive.
Why is it important to understand the lifecycle of indoor pests?
Understanding the lifecycle of indoor pests can help in identifying and effectively controlling them, as different stages may require different methods of extermination.
How long does the lifecycle of indoor pests usually last?
The lifecycle of indoor pests can vary greatly depending on the specific pest, but it typically ranges from a few weeks to several months.
Start your pest management today for a healthier home!
What are some common indoor pests and their lifecycles?
Common indoor pests include cockroaches, bed bugs, and mice. Cockroaches live for about 3-4 months, bed bugs for 6-12 months, and mice for 2-3 months.
Can indoor pests live all year?
Cockroaches can live indoors all year. They find food and shelter easily.
However, some pests simply can t handle the cold and may not survive the winter.






