Understanding the Life Cycle of Propagated Plants
Propagation is an essential process in horticulture, enabling you to cultivate new plants from those you already have.
In this article, you’ll explore several methods of propagation. These include seed, cutting, division, and grafting, each offering unique advantages based on your gardening style.
You ll discover key factors that influence propagation success. These include environmental conditions and plant health.
Contents
- Key Takeaways:
- Defining Propagation and Its Purpose
- Methods of Propagation
- Factors Affecting Propagation Success
- Stages of the Plant Life Cycle
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the life cycle of propagated plants?
- What are the different stages in the life cycle of propagated plants?
- What is propagation and how is it different from reproduction?
- Why is understanding the life cycle of propagated plants important?
- How long does it take for a propagated plant to reach maturity?
- What happens after a propagated plant reaches maturity?
Key Takeaways:
Defining Propagation and Its Purpose
Plant propagation is a key gardening practice. It involves techniques to grow new plants from existing ones. This allows you, as a gardener or plant enthusiast, to expand your collection and experience the profound joy that comes from nurturing new life.
Whether you choose to propagate through seeds, cuttings, or division, grasping the purpose behind these methods not only elevates your gardening skills but also deepens your connection with nature and contributes to biodiversity.
Methods of Propagation
Familiarize yourself with different propagation methods. Whether it’s seed propagation, cutting techniques, or division, each has unique benefits and challenges. Understanding these nuances will empower you to achieve successful propagation outcomes, enhancing your gardening expertise.
Seed Propagation
Seed propagation is all about planting seeds in the best possible conditions to encourage germination and growth. This method is essential for growing various plants, from vibrant herbs to beautiful flowers.
To start this rewarding endeavor, your first step is to select seeds with care, ensuring they are well-suited for your specific climate and soil type. Pay attention to the soil needs; quality soil enriched with organic matter is crucial, as it provides the nutrients your plants need for optimal growth.
Once you ve sown the seeds, managing germination techniques becomes vital. Keeping moisture levels and temperature just right is key to success. Resources from institutions like the University of New Hampshire can be invaluable, guiding you through best practices and conditions to ensure your seed propagation journey flourishes.
Cutting Propagation
Cutting propagation is a favored technique among plant enthusiasts, allowing you to take cuttings from mature plants and encourage them to develop roots a straightforward and effective way to expand your collection.
Select the right part of the parent plant for the best results. Look for healthy stems with leaves and a growth node; this is where new roots will emerge. Positioning your cuttings in a spot with indirect but bright light will significantly enhance their chances of developing robust roots. Utilizing filtered water can also be advantageous, as it helps prevent chloramine and fluoride from stunting growth.
If you re embarking on your first DIY propagation adventure, maintaining cleanliness and opting for small jars or containers can simplify the process, making it accessible even for beginners.
Division Propagation
Division propagation is a technique that allows you to separate mature plants into smaller sections. Each section can grow independently, promoting healthier plants and fostering fuller growth.
This approach is especially effective for perennials and certain houseplants. It s best performed in spring or fall when temperatures are moderate and plant growth is thriving. Timing is crucial; choose a moment when your plants aren t stressed by drought or extreme temperatures. Ensure that the soil is well-draining and enriched with organic matter before you begin.
After the division, your new sections will need consistent watering. Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged to avoid root rot. By monitoring these new plants closely, you can help them establish quickly. A light application of fertilizer will encourage vigorous re-rooting.
Grafting Propagation
Grafting propagation is an advanced gardening method that combines parts from different plants. This creates a new entity that enhances desirable traits while ensuring robust root growth.
This method harnesses the strengths of various species and promotes diversity within plant families. Different types of grafting, such as whip-and-tongue or cleft grafting, suit specific needs based on the plants involved, allowing for tailored outcomes.
The benefits are significant: grafting can lead to increased disease resistance, improved fruit yield, and earlier maturity. Successful grafting requires meticulous attention. Selecting the right rootstocks and parts that will grow into new plants, along with providing adequate aftercare, is crucial for promoting the overall health and vigor of grafted plants. Watch them thrive and show off their best traits!
Factors Affecting Propagation Success
The success of plant propagation hinges on key factors like environmental conditions, plant health, and genetics. Understanding their impact can significantly enhance your results.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions play a crucial role in your plant propagation efforts. Factors like light exposure and effective watering techniques are key to fostering healthy growth.
It’s important to know how light intensity affects plant growth. Indirect light is gentler, mimicking the dappled sunlight found in nature, making it perfect for tender seedlings. In contrast, bright light provides the energy that more robust plants need to photosynthesize effectively.
When considering these conditions, remember that best practices for watering depend on using a well-draining soil mix to avoid root rot while maintaining consistent moisture. Techniques like bottom watering can be particularly beneficial, encouraging your plants to extend their roots deep into the soil in search of water. This promotes a resilient root system and enhances overall plant vitality.
Plant Health and Genetics
Healthy plants with good genetics are key to successful propagation. When you nurture strong, well-cared-for plants, you can expect impressive results in terms of root development and overall vigor.
However, health issues like pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies can severely compromise propagation efforts. This can lead to weakened offspring or even the failure to produce new growth.
Genetics also play a pivotal role; specific genetic traits can either enhance or limit a plant’s ability to thrive in various environments. Regularly assess the health of your mature plants to keep them in peak condition. By ensuring optimal light, proper watering, and quality soil, you can prevent ailments that jeopardize propagation.
Incorporating organic fertilizers can offer the vital nutrients your plants need, bolstering their resilience and increasing the likelihood of producing robust propagules.
Start your propagation journey today and see the rewards for yourself!
Stages of the Plant Life Cycle
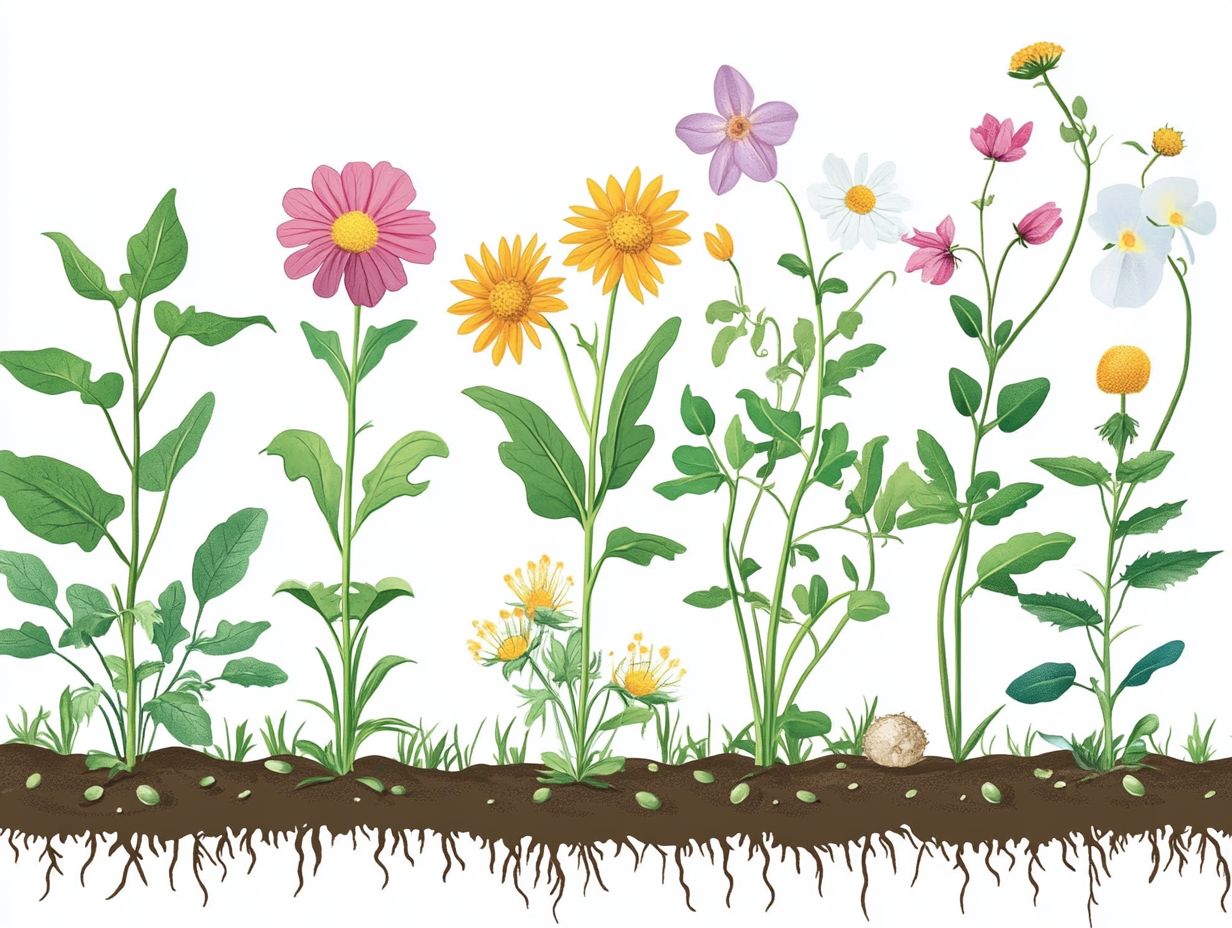

The plant life cycle unfolds through distinct stages: germination, growth and development, reproduction, and death and decay. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the continuity of plant life and its propagation.
Germination
Germination marks the initial stage of the plant life cycle. Here, seeds undergo essential transformations under specific environmental conditions, setting them on the path to maturity.
To achieve successful seed propagation, several key factors come into play. Ensure that the soil is well-aerated and rich in nutrients to support growth. Moisture levels are also crucial; seeds depend on a consistent supply of water to initiate the biochemical processes that lead to sprouting.
Light conditions can significantly influence germination rates. Some seeds flourish with exposure to light, while others prefer darkness. By managing these variables, you can enhance the chances of effective germination and foster the healthy growth of your plants.
Growth and Development
The growth and development stage is where you witness plants transitioning from seedlings to their mature forms. It demands your careful attention, adequate care, and the right conditions for thriving.
This phase is where the magic happens! It lays the groundwork for long-term health and productivity. Proper watering techniques are essential; both overwatering and underwatering can lead to stress or even root rot.
For nutrient management, ensure a balanced mix of large and small nutrients that plants need to grow. This will significantly impact growth rates and enhance resilience against pests.
Regularly monitoring soil moisture and nutrient levels will empower you to make timely adjustments, promoting strong root systems and lush foliage key elements for successful propagation and overall plant vitality.
Reproduction
Reproduction is a crucial phase in the plant life cycle. It allows you to cultivate seeds or new plantlets, ensuring the survival of the species and the potential for successful propagation.
This dynamic process varies among species and includes diverse strategies. For example, sexual reproduction is the process involving pollen transfer to create seeds, while asexual methods focus on cloning and developing offshoots. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for anyone involved in horticulture or gardening.
The care you provide during these stages like optimal watering, appropriate lighting, and careful management of nutrients can significantly boost your chances of successful propagation.
By employing proper practices, you pave the way for robust seedlings that thrive, blending knowledge with attentive care in your gardening journey.
Death and Decay
Death and decay are intrinsic components of the plant life cycle. They play a vital role in enriching the soil and enabling new growth, thus completing the cycle of propagation.
These processes ensure that nutrients once embedded within the plant are released back into the ecosystem, nurturing future generations of flora. The decomposition of organic matter like fallen leaves, stems, and roots creates rich humus that enhances soil structure and moisture retention, crafting a better environment for seeds to sprout.
As microorganisms break down this matter, they recycle essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus, elevating the soil’s overall fertility. Thus, death and decay are not merely an endpoint; they serve as a crucial beginning, forming the backbone of a sustainable ecosystem that consistently supports diverse plant life.
Frequently Asked Questions

Now that you understand the plant life cycle, why not start your own gardening journey? Use this knowledge to nurture your plants effectively!
What is the life cycle of propagated plants?
The life cycle of propagated plants includes the stages of growth and development from propagation to maturity. This process starts when a plant is reproduced through methods like cuttings or grafting.
What are the different stages in the life cycle of propagated plants?
The life cycle has several stages: propagation, establishment, growth, maturity, and reproduction. Each stage is crucial for the plant’s overall development.
What is propagation and how is it different from reproduction?
Propagation creates new plants from existing ones using methods such as cuttings or grafting. Reproduction, however, is a natural process involving male and female parts to produce offspring.
Why is understanding the life cycle of propagated plants important?
Knowing the life cycle helps gardeners and farmers manage their plants better. It guides them in choosing the right propagation methods and care at each growth stage.
How long does it take for a propagated plant to reach maturity?
The time to maturity varies by plant type, environmental conditions, and propagation method. It can range from a few months to several years.
What happens after a propagated plant reaches maturity?
A mature propagated plant can produce new plants through sexual reproduction. This continues the life cycle, going from reproduction to maturity and eventually to death.






